MammoScreen Project
MammoScreen is a project co-funded by the European Union and the UK Research and Innovation agency. It is set up with the aim of generating clinical evidence on the use of MammoWave®, a medical device based on microwave frequencies, for breast cancer prevention. The project involves seven international partners from Italy, Portugal, Spain and the UK.
MammoScreen aims to support the validation of an innovative, safe and non-invasive solution for the detection of breast cancers.
Discover the MammoScreen Project
OVERVIEW
An opportunity to advance in breast cancer detection

TECHNOLOGY
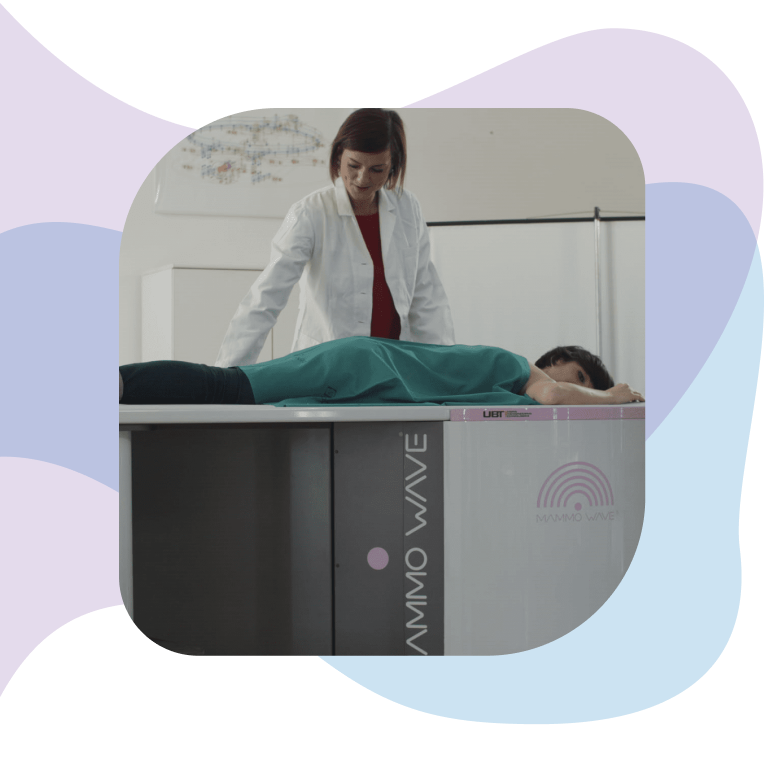
MammoWave®: a medical device for breast lesion detection
CITIZEN
MammoScreen’s collaborative approach empowers individuals to actively participate in shaping the future of healthcare, driving advancements, and improving patient outcomes.
Relevance and user-Centric Design
Citizens, especially those who have experienced breast cancer or have been screened for it, possess valuable insights and perspectives.
Acceptability and trust
By involving citizens, we ensure that they can contribute to the decision-making process and voice their concerns, thus enabling them to be part of the acceptance process of the technology.
Accessible and equitable Healthcare
By engaging citizens from different backgrounds, socioeconomic statuses, and geographical locations, MammoScreen hopes to identify and address potential inequities to access breast cancer screening.
Ethical considerations
Engaging citizens in the development and evaluation of MammoWave® helps addressing ethical concerns. Informed consent, privacy protection, and responsible data handling are essential aspects of any healthcare technology.
Advocacy and empowerment
By participating in the development and evaluation of this medical device, citizens can inform policies, raise awareness, and contribute to the improvement of breast cancer prevention, including screening programmes.
News and publications
Join our Community
Find out the latest news about MammoScreen world and stay up to date with the project.
1 M. Kalager, M. Zelen, F. Langmark, and H.-O. Adami, “Effect of Screening Mammography on Breast-Cancer Mortality in Norway,” New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 363, no. 13, pp. 1203–1210, Sep. 2010, doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1000727
Broeders, M., Moss, S., Nyström, L., Njor, S., Jonsson, H., Paap, E., Massat, N., Duffy, S., Lynge, E., & Paci, E. (2012). The Impact of Mammographic Screening on Breast Cancer Mortality in Europe: A Review of Observational Studies. Journal of Medical Screening, 19(1_suppl), 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1258/jms.2012.012078
2 Iwamoto, Y., Kaucher, S., Lorenz, E., Bärnighausen, T., & Winkler, V. (2019). Development of breast cancer mortality considering the implementation of mammography screening programs – a comparison of western European countries. BMC Public Health, 19(1), 823. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7166-6
3 C. Romero Castellano et al., “Breast cancer mortality after eight years of an improved screening program using digital breast tomosynthesis,” J Med Screen, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 456–463, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1177/09691413211002556
4 Tagliafico AS , Houssami N . Towards consensus on managing high mammographic density in population breast screening? Breast 2023;69:422–3:S0960-9776(23)00446-0. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2023.04.004
5Rana, S.P.; Dey, M.; Loretoni, R.; Duranti, M.; Ghavami, M.; Dudley, S.; Tiberi, G. Radiation-Free Microwave Technology for Breast Lesion Detection Using Supervised Machine Learning Model. Tomography 2023, 9, 105-129. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010010
6Álvarez Sánchez-Bayuela D, Ghavami N, Tiberi G, Sani L, Vispa A, Bigotti A, et al. , 2023, A multicentric, single arm, prospective, stratified clinical investigation to evaluate MammoWave’s ability in breast lesions detection. PLoS ONE 18(7): e0288312











